Animals, Agriculture & Food

Simple, Rapid and Inexpensive Process for Making Glue from Slaughterhouse Animal Blood
WARF: P07418US
Inventors: Sundaram Gunasekaran, Hai Lin
The Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation (WARF) is seeking commercial partners interested in developing a simple, rapid, cost-effective and novel process for making glue from whole blood.
Overview
Slaughterhouse blood is a waste product that must be disposed. Currently, the main use of this blood is for blood meal in animal feed.
Another option is to use the blood in glue. However, while techniques have been developed for making glue from waste animal blood, these techniques generally require drying the blood prior to use, an expensive and energy-consuming step. New methods for generating a consistent, strong and high-quality glue without first dehydrating the blood are needed.
Another option is to use the blood in glue. However, while techniques have been developed for making glue from waste animal blood, these techniques generally require drying the blood prior to use, an expensive and energy-consuming step. New methods for generating a consistent, strong and high-quality glue without first dehydrating the blood are needed.
The Invention
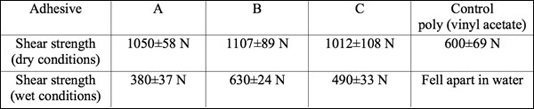
UW-Madison researchers have developed a novel and simple process for making glue from whole animal blood. The process starts by adding an anticoagulant and a preservative to fresh, whole blood. Then lime and sodium hydroxide are added, and the pH of the mixture is adjusted until it is between about 9 and 11. To yield the final adhesive, a curing agent and ammonia are added to the mixture. The resulting glue bonds well to surfaces, including paper, cardboard and wood.
Applications
- Laminates
- Plywood and particle board
- Mulch spray
- Wallpaper
- Furniture
- General adhesive, such as for cardboard boxes
Key Benefits
- Does not require a drying step before chemical modification
- Takes only 10 to 15 minutes
- Can be performed at room temperature
- Process is inexpensive and uses few added ingredients.
- Blood can come from any animal source, including cattle, swine, chicken and fish.
- Glue bonds well to a variety of surfaces.
Additional Information
For More Information About the Inventors
Tech Fields
For current licensing status, please contact Emily Bauer at [javascript protected email address] or 608-960-9842
Figures